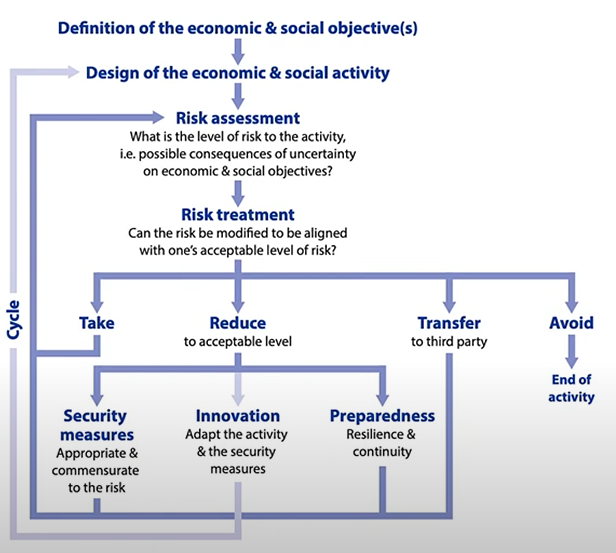
The overall process for managing security risk within an organization.
Several standards set out the process including accreditation(认证) and certification.
ISO/IEC 27001 is a standard that requires that an organization has:
Performed risk analysis to recognize their information assets and their associated information security risks based on threats, vulnerabilities, and impacts.
Designed and implement a coherent and comprehensive suite of information security controls and/or other forms of risk treatment to address those risks.
Designed and implement a coherent and comprehensive suite of information security controls and/or other forms of risk treatment to address those risks.
Adopted a management process to monitor, review and update risks and controls on an ongoing basis.
Other standards that are similar include Australia’s Protective Security Policy Framework (https://www.protectivesecurity.gov.au/) and NIST Cybersecurity Framework (https://www.nist.gov/cyberframework)
Establishing an ISMS(信息安全管理系统)
Many organisations implement an 27001-like security management system but unless you are doing it properly, i.e. to get certified
Although information security refers to non-digital assets, very few companies store non-digital information, Even if they use paper, it is archived digitally for example.
Security requirements come from 3 sources (ISO/IEC 27002):
Information security risks based on an organization's business strategy and objectives.
Legal, statutory(法定的), regulatory and contractual obligations.
The principles, objectives and business requirements for information processing that an organization has developed to support its operations.
Security Policy
Outlines an organizational approach to security through a set of policies that cover:
Internal organisation
Information security roles and responsibilities, segregation of duties, contact people.
Mobile devices and teleworking(远程办公).
Employment
Screening/onboarding, Information security awareness and training, disciplinary processes, termination.
Asset management
Media handling
Access control
User access management
System application access control
Cryptographic controls
Physical and environmental security
Operations security
Communications security
Systems acquisition, development and maintenance
Supplier relationships especially supply chain
Incident management
Business continuity
Risk Management
Assessing Risk
Qualitative (定性评估)
Quantitative (定量评估)
In both cases, need to understand:
The business itself
Assets of organisation
Threat analysis
Vulnerability assessment
Qualitative Risk Assessment (定性风险评估)
Uses a variety of techniques to assess risk:
Brainstorming
Delphi technique: anonymous question and answer technique (德菲儿问答,本质上是向企业主询问并获得答案)
Storyboarding (通过场景用例来分析)
Focus groups
Surveys/Questionnaires
Checklists
Can help in communication of risks but difficult to prioritise based on the range of values.
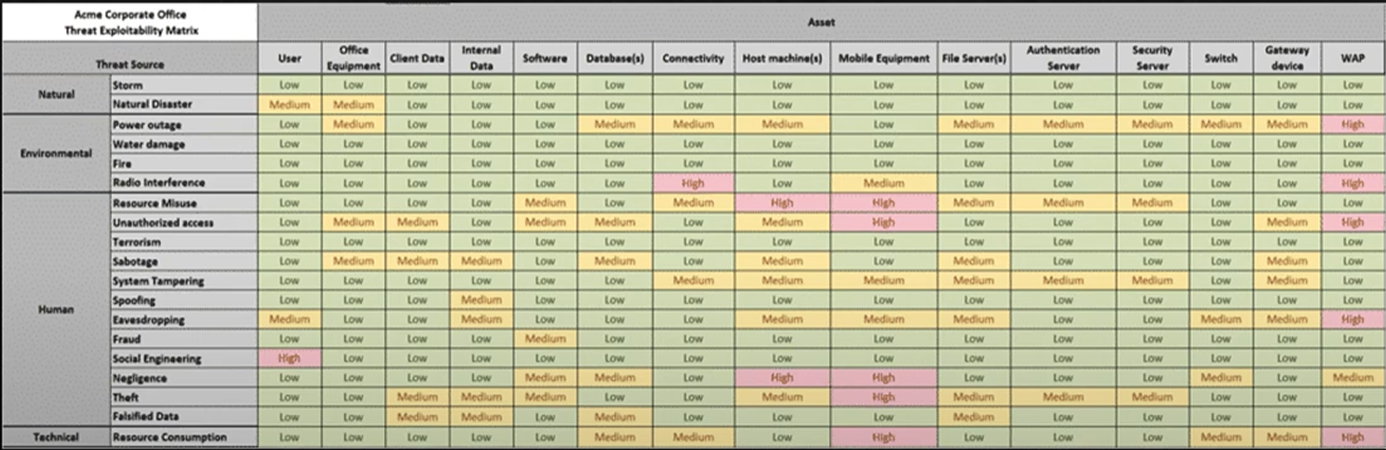
进行定性风险评估的流程:

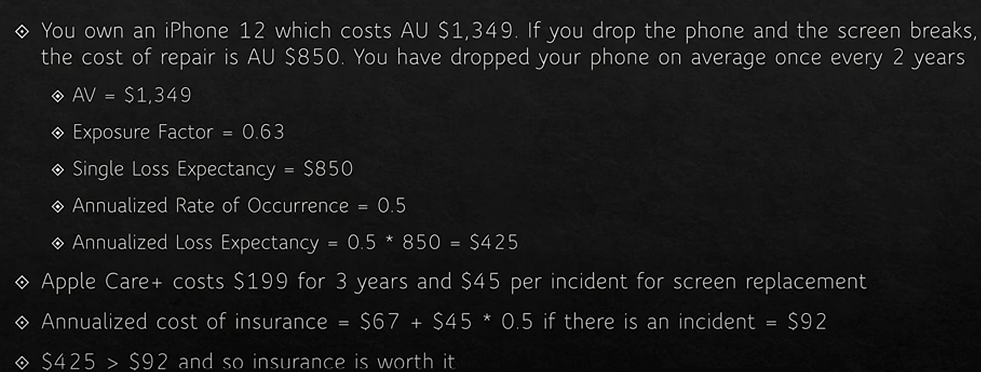
Open FAIR (定量风险评估)
FAIR is the Factor Analysis Information Risk adopted by the Open Group as an open standard
Quantitative risk analysis approach.
Main difference in this approach is that everything is expressed in probabilities and risk is:
Probable frequency and probable magnitude of loss
Vulnerability is the probability that a threat agent’s actions will result in a loss.
Controls are applied to risk and will reduce either
The frequency of threat actions
The magnitude(程度) of the loss
Risk Treatment
Once risks have been identified, they can be:
Reduced or mitigated
Use controls to reduce risk
Assigned or transferred
Transfer to a third party such as a cloud provider
Use cyberinsurance
Accepted
Accept the potential losses
Deterred (阻止)
Try and avoid the risk by using deterrences such as policies and warnings, security cameras, guards, fences, auditing etc.
Avoided
Change the business so that the risk is avoided. e.g. choose a different supplier or provider.
Rejected or ignored
Don’t accept the risk as being credible (dangerous move).
Risk Residual (剩余风险)
Once a risk is treated, the remaining risk is called residual risk.
So if total risk = threats × vulnerabilities × asset value
And the risk reduction from treatment is controlled risk(可控风险)
Then residual risk = total risk - controlled risk
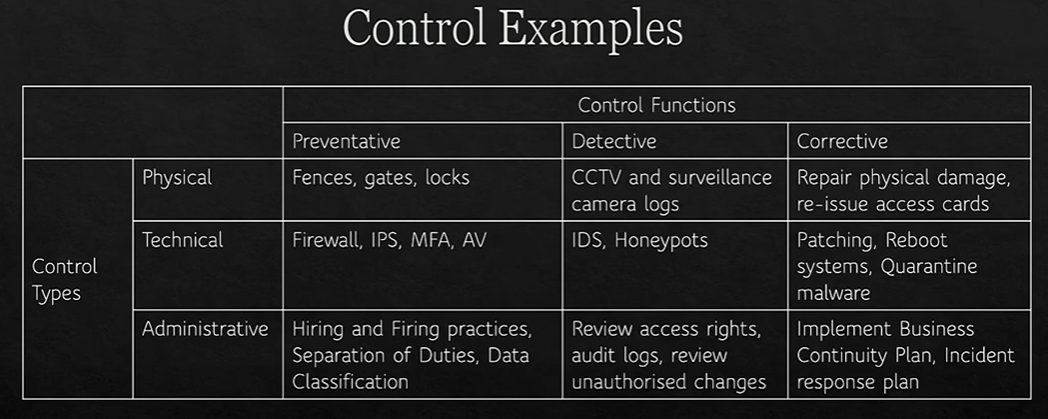
Controls
Controls are applied to mitigate cybersecurity risk
Types:
Physical
Technical
Administrative
Functions
Preventative
Detective
Corrective
Technical Controls
Technical, or logical, controls are the use of hardware or software to manage access provide protection to assets.
Examples include:
Authentication methods
Encryption
Anti-malware software
IDPS
Firewalls
Administrative Controls
Organisation's policies and procedures defined by its security policies
Focus on personnel and business practices
Examples include:
Hiring practices
Security screening
Data classification and labelling
Security awareness training
Physical Controls
Physical controls that prevent, monitor or detect unauthorised access to assets.
Examples include:
Lock systems
CCTV
Swipe cards
Mantraps (类似旋转门,一次只允许一个人进入,防止尾随)
Alarms
Deterrent Controls (威慑控制)
Discourages violation of security policies through visible warnings and consequences for violators.
Examples include:
Security-awareness training
Locks
Fences
Security badges
Guards
Mantraps
Security cameras
Preventive Controls
A control that aims to stop violation of security policies. Whilst similar to deterrence, preventive controls are far harder to casually violate than deterrence.
Examples include:
Locks
Biometrics
Alarm systems
Separation of duties
Data classification
Penetration testing
Access-control methods
Encryption
Auditing
Security policies
Security-awareness training
Anti-malware software
Firewalls
IPS
Detective Controls
Detective controls are concerned with detecting or discovering malicious activity during or after it has occurred.
Examples:
Audit trails
Logging
IDS
Honeypots (and honeynets)
CCTV
Summary:
Security Operations
Need-to-know and Least Privilege
Aim is to keep secrets secret.
Grant users and systems access only to data and resources they need for their specific duties.
Separation of duties and responsibilities
Never put a single person in charge of an entire function
Includes putting cybersecurity responsibilities outside of IT
Don’t want the people implementing systems also checking them
Two-person control, Job rotation, mandatory vacations
Privileged account management
Change management
Personnel security
Security awareness training
Mobile device management
Working from home
Information management lifecycle
Creation, storage, use, archiving, destruction and purging
Hardware and software
Asset management
Protection of physical assets
Machine rooms: access, cooling and fire prevention
Virtual assets
Licensing and Software License Agreements
